RDF: Accumulating g(r) for a Fluid¶
The freud.density module is intended to compute a variety of quantities that relate spatial distributions of particles with other particles. This example demonstrates the calculation of the radial distribution function \(g(r)\) for a fluid, averaged over multiple frames.
[1]:
import numpy as np
import freud
from util import box_2d_to_points
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
data_path = "data/phi065"
box_data = np.load("{}/box_data.npy".format(data_path))
pos_data = np.load("{}/pos_data.npy".format(data_path))
def plot_rdf(box_arr, points_arr, prop, rmax=10, dr=0.1, label=None, ax=None):
"""Helper function for plotting RDFs."""
if ax is None:
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(12, 8))
ax.set_title(prop, fontsize=16)
rdf = freud.density.RDF(rmax, dr)
for box, points in zip(box_arr, points_arr):
rdf.accumulate(box, points)
if label is not None:
ax.plot(rdf.R, getattr(rdf, prop), label=label)
ax.legend()
else:
ax.plot(rdf.R, getattr(rdf, prop))
return ax
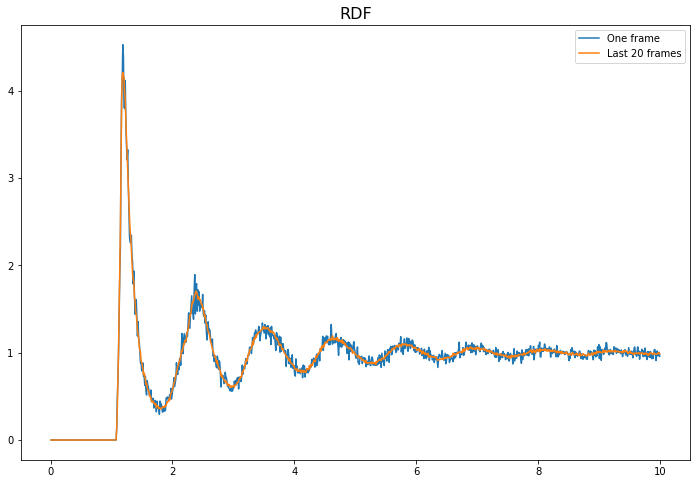
Here, we show the difference between the RDF of one frame and an accumulated (averaged) RDF from several frames. Including more frames makes the plot smoother.
[2]:
# Compute the RDF for the last frame
box_arr = [box_data[-1].tolist()]
pos_arr = [pos_data[-1]]
ax = plot_rdf(box_arr, pos_arr, 'RDF', dr=0.1, label='One frame')
# Compute the RDF for the last 20 frames
box_arr = [box.tolist() for box in box_data[-20:]]
pos_arr = pos_data[-20:]
ax = plot_rdf(box_arr, pos_arr, 'RDF', dr=0.1, label='Last 20 frames', ax=ax)
plt.show()
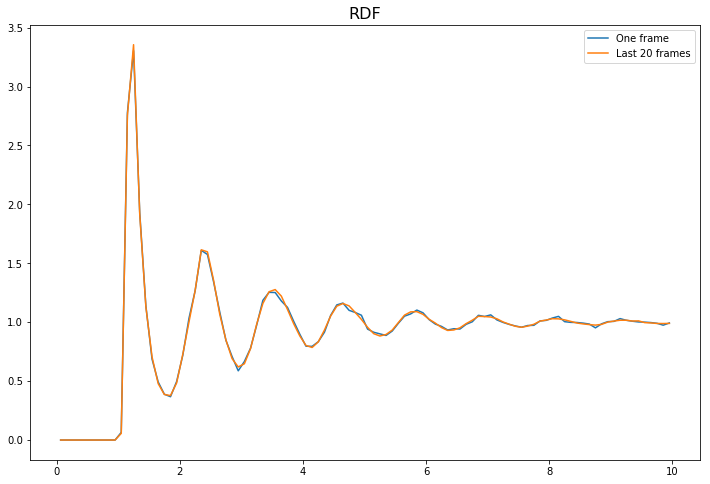
The difference between accumulate (which should be called on a series of frames) and compute (meant for a single frame) is more striking for smaller bin sizes, which are statistically noisier.
[3]:
# Compute the RDF for the last frame
box_arr = [box_data[-1].tolist()]
pos_arr = [pos_data[-1]]
ax = plot_rdf(box_arr, pos_arr, 'RDF', dr=0.01, label='One frame')
# Compute the RDF for the last 20 frames
box_arr = [box.tolist() for box in box_data[-20:]]
pos_arr = pos_data[-20:]
ax = plot_rdf(box_arr, pos_arr, 'RDF', dr=0.01, label='Last 20 frames', ax=ax)
plt.show()