Benchmarking Neighbor Finding against scipy#
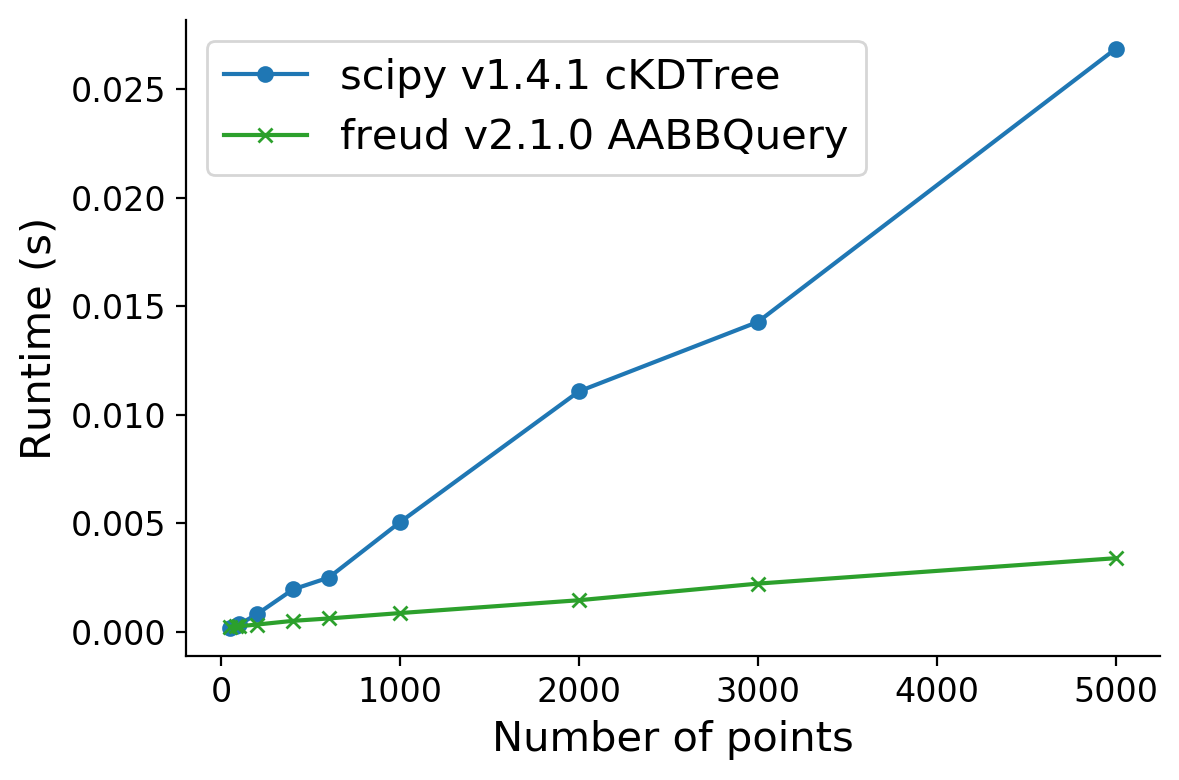
The neighbor finding algorithms in freud are highly efficient and rely on parallelized C++ code. Below, we show a benchmark of freud’s AABBQuery algorithm against the scipy.spatial.cKDTree. This benchmark was run on an Intel(R) Xeon(R) i3-8100B CPU @ 3.60GHz.
[1]:
import timeit
import freud
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import scipy.spatial
from tqdm.notebook import tqdm
[2]:
def make_scaled_system(N, Nneigh=12):
L = (4 / 3 * np.pi * N / Nneigh) ** (1 / 3)
return freud.data.make_random_system(L, N)
box, points = make_scaled_system(1000)
Timing Functions#
[3]:
def time_statement(stmt, repeat=5, number=100, **kwargs):
timer = timeit.Timer(stmt=stmt, globals=kwargs)
times = timer.repeat(repeat, number)
return np.mean(times), np.std(times)
[4]:
def time_scipy_cKDTree(box, points):
shifted_points = points + np.asarray(box.L) / 2
# SciPy only supports cubic boxes
assert box.Lx == box.Ly == box.Lz
assert box.xy == box.xz == box.yz == 0
return time_statement(
"kdtree = scipy.spatial.cKDTree(points, boxsize=L);"
"kdtree.query_ball_tree(kdtree, r=rcut)",
scipy=scipy,
points=shifted_points,
L=box.Lx,
rcut=1.0,
)
[5]:
def time_freud_AABBQuery(box, points):
return time_statement(
"aq = freud.locality.AABBQuery(box, points);"
"aq.query(points, {'r_max': r_max, 'exclude_ii': False}).toNeighborList()",
freud=freud,
box=box,
points=points,
r_max=1.0,
)
[6]:
# Test timing functions
kd_t = time_scipy_cKDTree(box, points)
print(kd_t)
abq_t = time_freud_AABBQuery(box, points)
print(abq_t)
(0.6436181232333184, 0.008598492136056879)
(0.09153120275586843, 0.00780408130095089)
Perform Measurements#
[7]:
def measure_runtime_scaling_N(Ns, r_max=1.0):
result_times = []
for N in tqdm(Ns):
box, points = make_scaled_system(N)
result_times.append(
(time_scipy_cKDTree(box, points), time_freud_AABBQuery(box, points))
)
return np.asarray(result_times)
[8]:
def plot_result_times(result_times, Ns):
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6, 4), dpi=200)
ax.plot(
Ns,
result_times[:, 0, 0] / 100,
"o",
linestyle="-",
markersize=5,
label=f"scipy v{scipy.__version__} cKDTree",
)
ax.plot(
Ns,
result_times[:, 1, 0] / 100,
"x",
linestyle="-",
markersize=5,
c="#2ca02c",
label=f"freud v{freud.__version__} AABBQuery",
)
ax.set_xlabel(r"Number of points", fontsize=15)
ax.set_ylabel(r"Runtime (s)", fontsize=15)
ax.legend(fontsize=15)
ax.spines["top"].set_visible(False)
ax.spines["right"].set_visible(False)
ax.tick_params(axis="both", which="both", labelsize=12)
fig.tight_layout()
return fig, ax
[9]:
# Use geometrically-spaced values of N, rounded to one significant figure
Ns = list(
sorted(
set(
map(
lambda x: int(round(x, -int(np.floor(np.log10(np.abs(x)))))),
np.exp(np.linspace(np.log(50), np.log(5000), 10)),
)
)
)
)
[10]:
result_times = measure_runtime_scaling_N(Ns)
fig, ax = plot_result_times(result_times, Ns)